- Basic + Advance Concept
*Each section involves practice of calculation and application of geometric tolerances.
**Brief comparison of ASME 2009 Y14.5 and ISO will be done.
- Course fee Includes 6 months of membership and Telephonic Personal consultation for any GD&T and Tolerance Stack-up related issue.
- For Company – Drawing review and Expert Suggestions, Design and detail engineering Mentorship
Engineering Drawing and GD&T
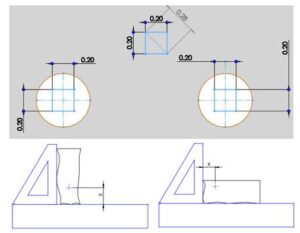
- Engineering Drawings
- Introduction to Dimensioning
- Dimensioning Rules
- Co-Ordinate Dimensioning System
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing system Myths in GD&T
Definitions and Symbols
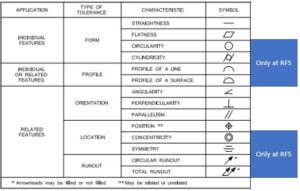
Rules and Different concepts of GD&T
- Limit of size
- Rule#1
- Rule#2
- Virtual condition
- Resultant Condition
- Effect of RFS
- Effect of MMC
- Effect of LMC
- Bonus Tolerance
Tolerance selection
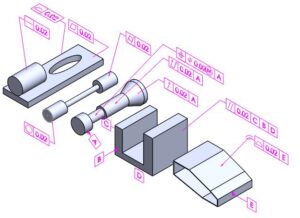
From Tolerance

- How to select Form Tolerance
- Straightness tolerance
- Flatness tolerance
- Circularity
- Cylindricity tolerance
- Application over a limited length area
Datum selection
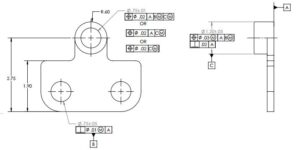
- How to select Datum for Feature of Control
- Datum feature
- Datum identification
- Temporary Datum and permanent Datum
- Datum reference Frames
- Datum simulator
- Planar datum
- Datum feature of RMB
- Maximum Material boundary
- Least material boundary
- Datum shift
- Translation modifier
- Effects of shuffling datum in a feature control frame
- Datum targets
- Single axis of two coaxial feature pr single datum plan
- Partial surface of Datum
- Rotational constrain due to axis
- Simultaneous requirement
- Restrained condition
- Identification
- Customized reference frame
Positional Tolerance

- How to select Location Tolerance
- Tolerance of location-positional tolerance
- Positional tolerance-RFS
- Positional tolerance -MMC
- Positional tolerance-LMC
- Multiple segment and composite tolerance
- Composite tolerance
- Multiple single segment tolerance
- Application of projected tolerance zone
- Application of positional tolerance to counter bores different positional tolerance at end faces to non-circular features
- Coaxial control of pattern feature of size
- Simultaneous requirement
- Coaxial feature of size
- Positional coaxial control
- Concentricity
- Symmetrical relationship
- Controlling symmetrical relationship by position
- Symmetry tolerance
Tolerance of profile
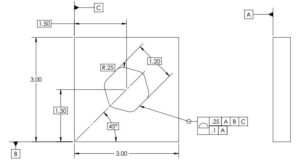
- How to select Profile tolerance
- Profile tolerance
- Uniform profile tolerance zone
- Bilateral tolerance
- Unilateral and unequal bilateral
- All around and all over symbols
- Different tolerance for different segment of cross section
- Non uniform tolerance zone
- Composite Tolerance application
- Composite tolerance application to single features
- Composite tolerance application for feature in pattern
- No datum is in lower segment of the composite frame
- Primary datum A is repeated in lower segment of the composite frame
- Primary and secondary Datum are repeated in lower segment of the composite frame
- Individual feature control within feature in the pattern
- Application of profile tolerance
Orientation tolerance
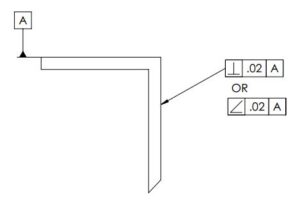
- How to select Profile tolerance
- Orientation tolerances
- Angularity
- Parallelism
- Perpendicularity
- Tolerance zone for orientation tolerance
- Orientation tolerance @MMC modifier
- Zero orientation Tolerances @MMC modifier
- Projected tolerance
- Projected tolerance
Runout tolerance
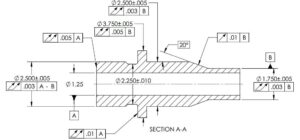
- How to select Runout tolerance
- Tolerance of Runout
- Datum section for Runout
- Circular runout
- Total runout
- Multiple Datum to control Runout control of datum surface
- Flat surface on datum
- Application of circular runout on a curved surface
Tolerance
- What, Why
- Limits- Fits and Tolerances
- Precision and Accuracy
- Various Fits
Tolerance Stack-up
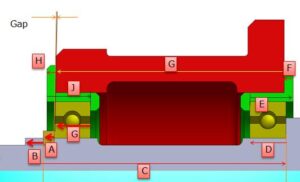
- Myths in Tolerance Stack-up
- What is tolerance Stack-up Analysis?
- Why to do tolerance Stack-up Analysis?
- Benefits tolerance Stack-up Analysis
- What are the driving factors in Stack-up analysis
- Assumptions and ways of doing stack-up
- Steps to be followed
- Rules preparing Loop diagram
- Converting all toleracing system to equal bilateral system
Examples Practice (Part Level and Assembly Level)
Fixed and Floating Formulas and Concept
Converting GD&T to Normal ± tolerance to use in stack-up analysis
- Few terminologies (VC, RC, OB and IB, Datum shift)
- Form Tolerances – To include in Tolerance stack-up or not
- Orientation Tolerances on surface and on feature of size
- Profile (Composite tolerance effect as well)
- Positional Tolerance (Composite tolerance, when and how to include segments)
- Datum shift assumption in Tolerance Stack-up
- Runout Consideration
- Symmetry and Concentricity
Radial Tolerance Stack-up
Part With Dimension and tolerance at an angle
Statistical Tolerancing (RSS and MRSS)





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.